Supported Storage Providers
- Local filesystem
- AWS S3
- DigitalOcean Spaces
- Google Cloud Storage
- Azure Blob Storage
- Minio
AWS S3
When using STORAGE_PROVIDER=s3 (for AWS S3, DigitalOcean Spaces, Minio, etc.), the underlying AWS SDK for JavaScript v3 handles authentication and configuration automatically based on its standard credential provider chain and region discovery:
- Credentials: Provide credentials via environment variables (
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY, and optionallyAWS_SESSION_TOKEN), a shared credentials file (~/.aws/credentials), or an IAM role (on EC2/ECS/Lambda). - Region: Specify the AWS region using the
AWS_REGIONenvironment variable or a shared config file (~/.aws/config). - S3-Compatible Endpoint: For services like Minio or DigitalOcean Spaces, you may also need to set the
S3_ENDPOINTenvironment variable to the service’s specific endpoint URL (e.g.,http://localhost:9000for local Minio, orhttps://nyc3.digitaloceanspaces.comfor DigitalOcean). - Max sockets: Optionally, set the
S3_MAX_SOCKETSenvironment variable to control the maximum number of concurrent connections to the storage service. This can be used to fine-tune performance based on your environment’s capabilities.
AWS credentials and configuration are loaded as described in the AWS SDK documentation:
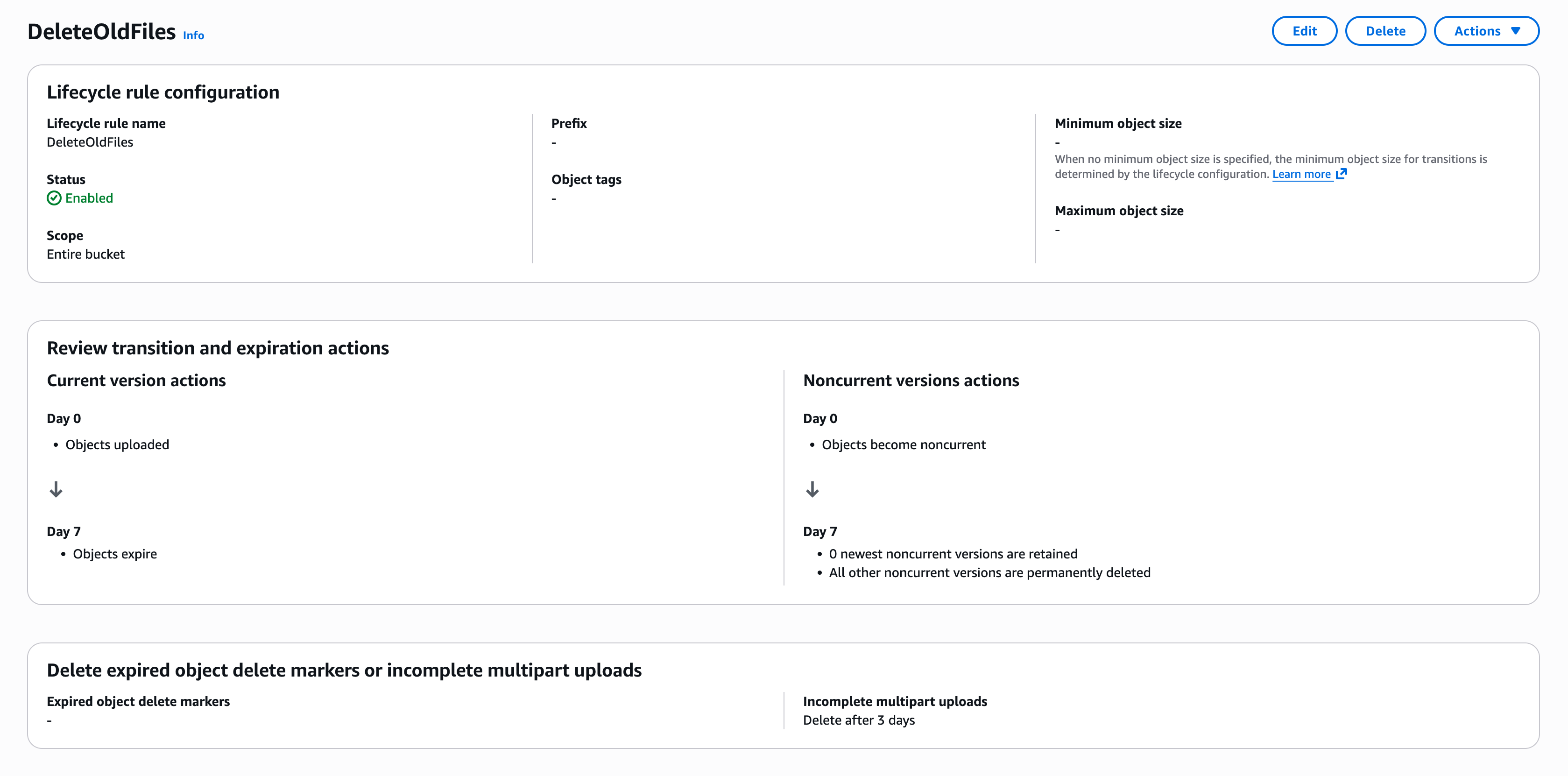
You should consider adding a lifecycle rule to your bucket in order to remove stale cache data and prevent your bucket from growing infinitely. Here’s a simple configuration that removes old objects after 7 days:
DigitalOcean Spaces
DigitalOcean Spaces is an S3-compatible object storage that this project also supports.
- Create a Space.
- Generate a new spaces access key.
- Fill in the
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDandAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYenvironment variables based on the access key you created. - Set
AWS_REGIONtous-east-1- Explanation - Set
STORAGE_PATHto the name of the Space you created. - Set
S3_ENDPOINTto the endpoint of the Space you created. For example,https://nyc3.digitaloceanspaces.com. - Set
STORAGE_PROVIDERtos3. - Optionally, set
S3_MAX_SOCKETSto control the maximum number of concurrent connections to the Space.
Google Cloud Storage
- Create a bucket (or use an existing one).
- Create a new service account.
- Grant the role
Storage Object Adminto the service account on the bucket.# .env STORAGE_PROVIDER=google-cloud-storage STORAGE_PATH=<name-of-the-bucket>Using static Service Account credentials
- Click “Create Key” and save the JSON file.
- Add the
project_id,client_email, andprivate_keyfrom saved JSON file to.env(or wherever you manage your environment variables):# .env GCS_PROJECT_ID=<project_id> GCS_CLIENT_EMAIL=<client_email> GCS_PRIVATE_KEY=<private_key>Using Application Default Credentials (ADC)
- Do not set
GCS_*environment variables# .env GCS_PROJECT_ID= GCS_CLIENT_EMAIL= GCS_PRIVATE_KEY=
Azure Blob Storage
- Create a new Blob Storage.
- On “Security + networking” tab, copy one of
Connection stringon “Access keys” blade. - Set
ABS_CONNECTION_STRINGto the connection string.
Minio
- Create Access key
- Fill in the
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDandAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYenvironment variables based on the access key you created. - Create bucket
- Set
STORAGE_PATHto the name of the bucket you created. - Set
AWS_REGION(can leave blankS3_REGION=for none). - Set
STORAGE_PROVIDERtominio. - Set
S3_ENDPOINTto Minio url (iehttp://127.0.0.1:9000) - Optionally, set
S3_MAX_SOCKETSto control the maximum number of concurrent connections to the Minio instance.